(1 point) The vector equation r (u,v) = u cOS vi + u … SolvedLib
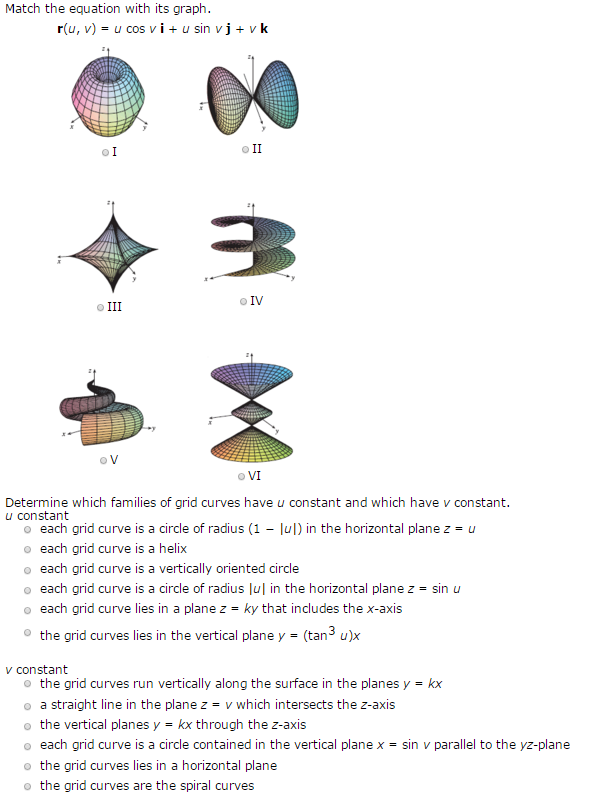
Match The Equation With Its Graph. R(u, V) = U Cos...
De nition 1. A parametrization is a function from a domain D in the uv plane into R3, written as ~r(u; v) = hx(u; v); y(u; v); z(u; v)i where x = x(u; v), y = y(u; v) and z = z(u; v) are real valued continuous functions (usually di erentiable, and often with additional assumptions). Those three real valued functions are called parametric equations.
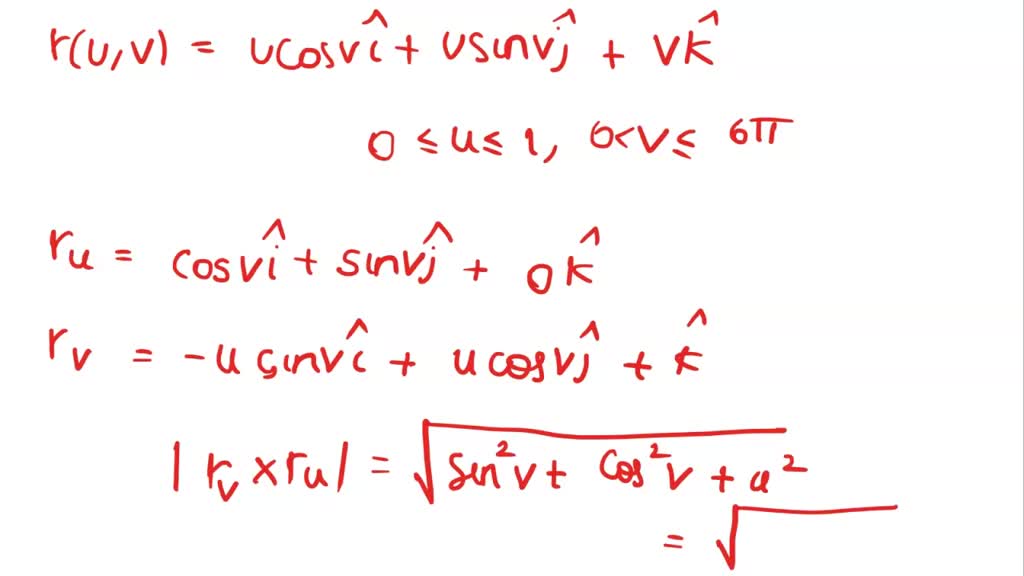
SOLVED point) The vector equation r (u, v) u COS vi + usin vj + vk; 0
The normal unit vector will be n^(x, y, z) =n^(φ(u, v)) = φu(u, v) ×φv(u, v) ∥φu(u, v) ×φv(u, v)∥ n ^ ( x, y, z) = n ^ ( φ ( u, v)) = φ u ( u, v) × φ v ( u, v) ‖ φ u ( u, v) × φ v ( u, v) ‖ but if you use the same parameterization to transform the surface integral to a 2d integral you get
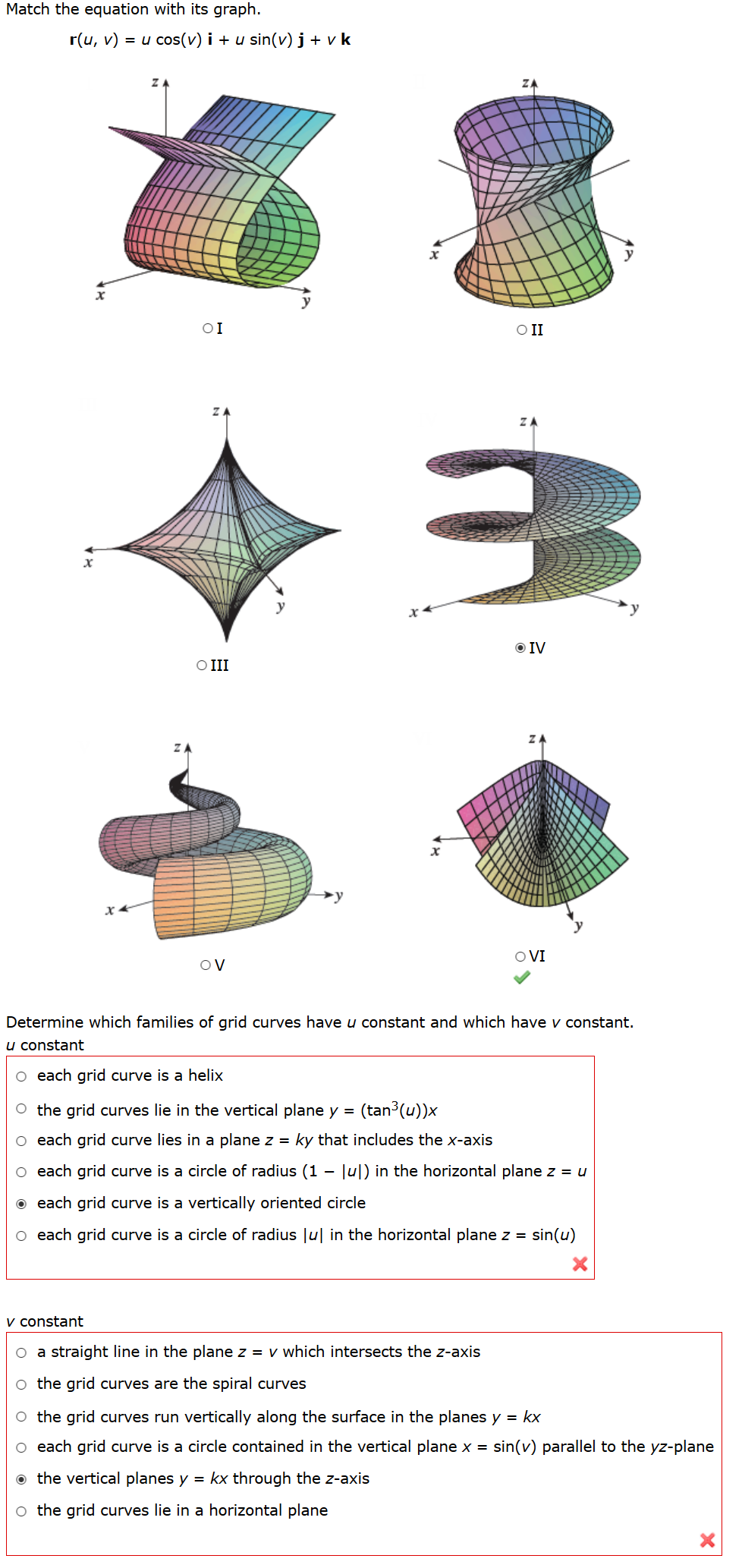
Solved Match the equation with its graph. r(u, v) = u cos(v)
Suppose that r( u,v) is a regular parametrization of a surface. Since the crossproduct r u ×r v is orthogonal to both r u and r v, the vector r u ×r v is normal to the surface at r( u,v) . It follows that the unit vector

M.R.U.V / PARTE 2 YouTube
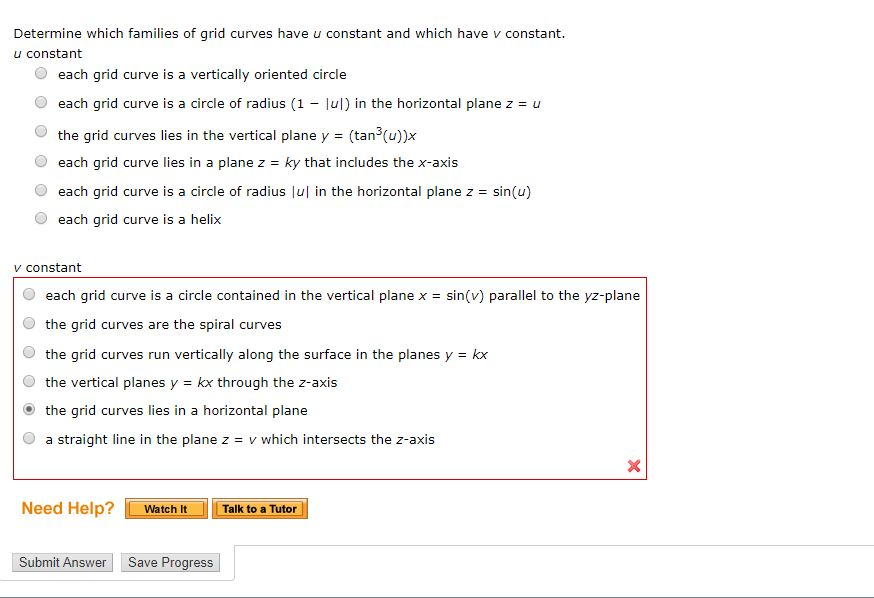
Standard Parameterized Surfaces Planes The plane through a point with has parametric equation r(u, v) = r0 + uu + vv, u, v 2 R The grid lines are parallel to u, v. Equivalent vector. The blue lines in the picture are the grid lines with u = 0, u = 1 and u = 2 respectively. The orange lines are v = 0, v = 1 and v = 2.

R.U.V. Rover Utility Vehicle Overview Utility vehicles, Lego space, Classic space
The problem of tracking with very long range radars is studied in this paper. First, the measurement conversion from a radar's r-u-v coordinate system to the Cartesian coordinate system is discussed.

Alphabet 20 A B C D E F G H I J K L m N O P Q R S T U V W … Flickr
Mit der R+V-Auslandsreise-Krankenversicherung gehen Sie auf Reisen kein Risiko ein. Auch im Skiurlaub. Ab 10,80 EUR pro Jahr. Zur Auslandsreise-Krankenversicherung Beitrag berechnen Hardwareversicherung Schutz für Computer und Co. Der Top-Elektronikschutz für alle PCs, Laptops, Spielekonsolen inklusive Originalzubehör und nachgerüstetem Zubehör.
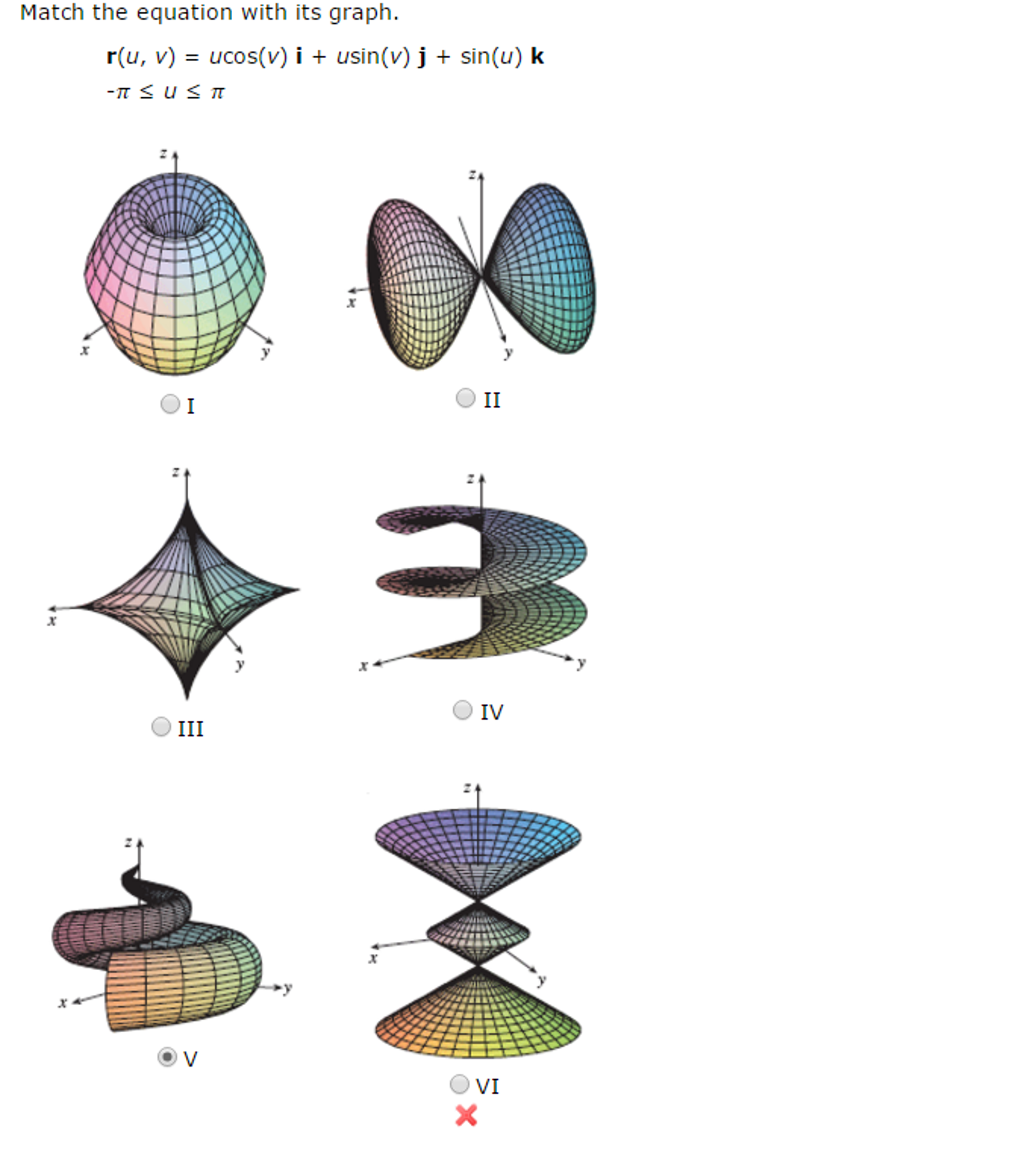
Solved Match the equation with its graph. r(u, v) = u
De nition: If the rst parameter uis kept constant, then v7!~r(u;v) is a curve on the surface. Similarly, if vis constant, then u7!~r(u;v) traces a curve the surface. These curves are called grid curves.

Solved Find the fundamental vector product for r(u, v) =
Electric power can be expressed as P = electrical power (watts, W) The power consumed in the electrical circuit above can be calculated as P = (12 volts) / (18 ohm) electric light bulb is connected to a supply. The current flowing can be calculated by reorganizing I = P / U = (100 W) / (230 V) 0.43 The resistance can be calculated by reorganizing

Pertamina RU V Balikpapan Dukung Kesiapan Menghadapi Nataru Pertamina
The parameterized surface is a vector valued function r ( u, v) of two variables, whether written in ijk vector notation or as an ordered triple of functions of u and v. Since each of the variables u and v ranges over an interval, the domain for r ( u, v) is a coordinate rectangle, say [ a, b ] x [ c, d ], in the uv -plane.

Pertamina RU V Pemasok 90 BBM ke PapuaMaluku Radar Sorong
Summary. This update automatically applies Safe OS Dynamic Update to the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) on a running PC to address a security vulnerability that could allow attackers to bypass BitLocker encryption by using WinRE. For more information, see CVE-2024-20666.
Solved Match the equation with its graph r(u, v) = sin(v) i
#ThorMotorCoach #VegasRV #RUVGreat adventures all start somewhere. Why not start yours in a Thor Vegas R.U.V. It's fully equipped and easy to drive. If a C.

(1 point) The vector equation r (u,v) = u cOS vi + u … SolvedLib
Example 16.6. 1: Consider the function r ( u, v) = v cos u, v sin u, v . For a fixed value of v, as u varies from 0 to 2 π, this traces a circle of radius v at height v above the x - y plane. Put lots and lots of these together,and they form a cone, as in Figure 16.6.1. Figure 16.6.1.

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z YouTube
If r(u;v) is the parameterization of a surface, then the surface unit normal is de-ned n = r u r v jjr u r vjj The vector n is also normal to the surface. surf3 Moreover, n is often considered to be a function n(u;v) which assigns a normal unit vector to each point on the surface. EXAMPLE 4 Find the surface unit normal and the equation of
ENEM Mapa Mental Gráficos M R U V Física
derivations of such models for constant-velocity problems in a variety of 2D polar and r-u coordinates systems and in 3D spherical and r-u-v coordinate systems, sparing tedious derivations for simple tracking problems. The conversions for r-u and r-u-v coordinate systems do not appear to have been previously published.
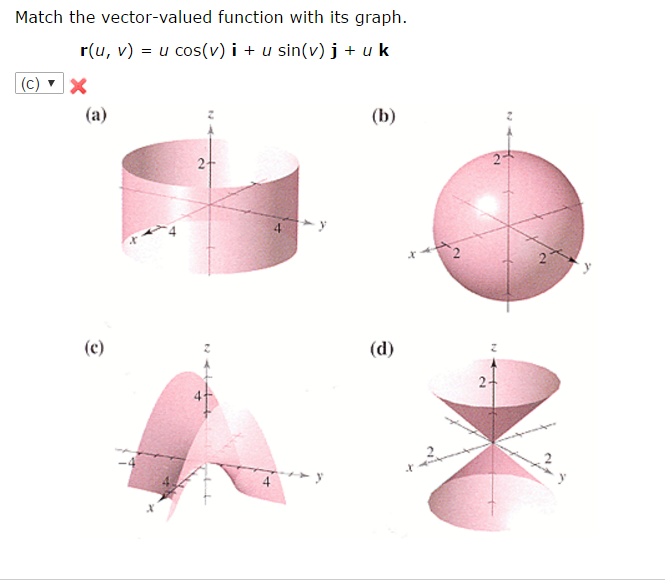
Solved Match the vectorvalued function with its graph. r(u,
Figure 16.6.6: The simplest parameterization of the graph of a function is ⇀ r(x, y) = x, y, f(x, y) . Let's now generalize the notions of smoothness and regularity to a parametric surface. Recall that curve parameterization ⇀ r(t), a ≤ t ≤ b is regular (or smooth) if ⇀ r ′ (t) ≠ ⇀ 0 for all t in [a, b].

Alphabet 01 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V Free Download Nude Photo Gallery
In this section we introduce the idea of a surface integral. With surface integrals we will be integrating over the surface of a solid. In other words, the variables will always be on the surface of the solid and will never come from inside the solid itself. Also, in this section we will be working with the first kind of surface integrals we'll be looking at in this chapter : surface.